The Excel PV function is used to return the present value of an investment based on a constant interest rate and payments.
The syntax for the PV function is:
=PV(rate, nper, pmt, [fv], [type])
| Argument | Purpose |
|---|---|
| rate | The interest rate per period of the investment |
| nper | The number of payments for the investment |
| pmt | The payment made each period |
| fv | The future value, or total remaining after the last payment has been made.This argument is optional, and if omitted the total is assumed to be 0 |
| type | When the payments are due. It can be entered as 1 or 0 and is optional. If omitted the value is assumed to be 00 – Payments are made at the end of the period1 – Payments are made at the beginning of the period |
The examples below show the PV function being used to return the present value dependent upon different parameters.
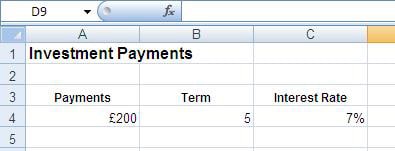
| Function | Result |
|---|---|
| =PV(C4/12,B4*12,A4) | £10,100Present value returned on an investment paid in £200 monthly payments for 5 years. Payments are made at the end of each period |
| =PV(C4/12,B4*12,A4,,1) | £10,159Present value returned on an investment paid in £200 monthly payments for 5 years. Payments are made at the beginning of each period |
| =PV(C4/52,B4*52,A4) | £43,850Present value returned on an investment paid in £200 weekly payments for 5 years. Payments are made at the end of each period |